PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
white to off-white crystalline powder
APPLICATIONS
APPEARANCE
white to off-white crystalline powder
98.0% min
MELTING POINT
|
|
|
| alpha-HYDROXY-ISOBUTYRIC ACID | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 594-61-6 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 209-848-8 | |
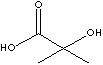
| FORMULA | (CH3)2C(OH)COOH | |
| MOL WT. | 104.11 | |
| H.S. CODE | ||
| TOXICITY | ||
| SYNONYMS | 2-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanoic acid; 2-Methyllactic acid; | |
| 2-Hydroxy-2-methylpropionic acid; 2-Hydroxyisobutyric acid; Acetonic acid; Hydroxydimethylacetic acid; ácido 2-hidroxi-2-metilpropionico; Acide 2-hydroxy-2-méthylpropionique; | ||
| RAW MATERIALS |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE |
white to off-white crystalline powder |
|
| MELTING POINT | 77 - 81 C | |
| BOILING POINT | 212 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
|
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | 1900 g/l (soluble in methanol, diethyl ether, sparingly soluble in benzene) | |
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
| NFPA RATINGS | ||
| FLASH POINT |
|
|
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. Hygroscopic. | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| n-Butyric acid is a saturated four-carbon carboxylic acid which is a clear liquid, with a suffocating odor and with melting point -6 C and boiling point 164 C. It occurs naturally in rancid butter, in much animal fat and in plant oil. It is soluble in water, ethanol and ether. It can be obtained by the fermentation of sugar or starch, brought about by the addition calcium carbonate or by the oxidation of butanol in the presence of potassium permanganate. There is a structural formula called isobutyric acid which can not be obtained by the fermentation but by the oxidation of isopropyl alcohol with potassium bichromate and sulfuric acid. Isobutyric acid melts at -47 C and boils at 154 C. It is slightly soluble in water but soluble in ethanol, ether and organic solvents. Butyric acid is a strong acid and reacts with bases, strong oxidants and metals. It is used to eliminate calcium in leather industry. Butyric acid family products, such as their esters, are used for the production of plastics, plasticizers, surfactants and textile auxiliaries. They are used in food additives, flavorings, varnishes, perfumes, pharmaceuticals and disinfectants. Aminobutyric acid is a four-carbon carboxylic acid, to which an amino group is attached. There are three structural isomers, alpha, beta, gamma-. Alpha-aminobutyric acid is has an amino group substituted at the alpha, or 1 position on the carbon atom next to the acid group, while gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) at the terinal carbon (the gamma, or 4 position). Natural GABA exits in L-form only and can be found in plant and animal tissues. It is formed in the metabolism of L-glutamic acid. It is the central nervous system postsynaptic inhibitory transmitter in the brain but is also found in several extraneural tissues, including kidney and pancreatic islet beta cells. Gamma- hydroxy butyric acid is an intermediate occurring in metabolism of GABA. There are several hydroxy butyric acid occur at elevated levels in some metabolic disorders. In biological systems The GABA family products are the parent compounds for a number of psychoactive drugs covering sedation/hypnosis, anxiolysis, anticonvulsant activity, muscle relaxation and anterograde amnesia. Some examples are benzodiazepines, baclofen, bicuculline, barbiturates, picrotoxin, neurosteroids and the general anesthetics. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white to off-white crystalline powder |
|
| CONTENT |
98.0% min |
|
|
MELTING POINT |
77 - 81 C | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | ||
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 37/38-41, Safety Phrases: 26-39 | ||
|
|
|